The IEC 61850 protocol has become the global standard for substation automation, enabling high-speed communication, interoperability, and streamlined integration of intelligent electronic devices (IEDs). It plays a foundational role in transforming traditional substations into digital substations that support real-time control, monitoring, and automation across the electrical grid.
What Is the IEC 61850 Protocol?
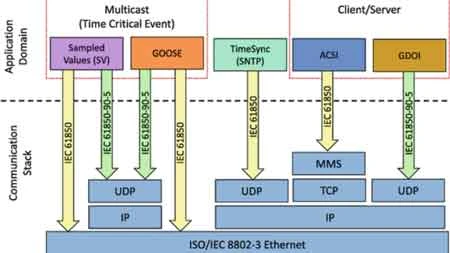
IEC 61850 is a communications protocol developed by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) for automated substation systems. Unlike older legacy protocols that rely on fixed, vendor-specific formats, IEC 61850 uses an object-oriented data model and abstract communication services to create a standardized method for data exchange among IEDs, SCADA systems, and Human-Machine Interfaces (HMIs).
Its architecture is based on Ethernet and supports both client-server and peer-to-peer communications, making it ideal for smart grid applications that require high-speed, deterministic messaging.
Key Features of the IEC 61850 Protocol
The success of IEC 61850 in modern substation automation is driven by several key features that distinguish it from older communication standards. These capabilities support high-speed event handling, structured data modeling, and network flexibility.
Interoperability Across Devices
IEC 61850 enables seamless integration of equipment from multiple manufacturers by defining common data structures and naming conventions. This interoperability reduces engineering time and ensures long-term system flexibility.
High-Speed Messaging with GOOSE
The protocol includes GOOSE messaging (Generic Object-Oriented Substation Events), which allows IEDs to communicate critical event data in under 4 milliseconds. These peer-to-peer messages operate at the Ethernet layer, making them ideal for protection and control schemes.
Process Bus and Station Bus Architecture
IEC 61850 divides communication into two logical layers:
Station Bus: Handles data exchange between IEDs, SCADA, and HMIs using MMS (Manufacturing Message Specification).
Process Bus: Replaces traditional copper wiring by transmitting sampled values (SV) and control signals between field equipment and IEDs over Ethernet via Merging Units (MUs).
Scalable Data Modeling
The standard uses Logical Nodes and Logical Devices to define all data points in a substation. This object-oriented modeling enables efficient configuration, simplified diagnostics, and faster system deployment.
Time Synchronization
IEC 61850 supports Precision Time Protocol (PTP) to align time-sensitive operations across devices, which is essential for fault analysis, event recording, and system coordination.
Benefits of the IEC 61850 Protocol
Beyond its technical specifications, IEC 61850 delivers significant operational and economic advantages to utilities and grid operators. These benefits make it a strategic choice for modernizing substation infrastructure.
Reduced wiring complexity and installation costs
Improved protection system response through fast GOOSE messaging
Vendor-agnostic system design
Future-proofing with support for emerging smart grid technologies
Easier integration of renewable energy, energy storage, and microgrids
Enhanced cybersecurity through standards such as IEC 62351
GOOSE Messaging: Real-Time Communication
A standout innovation in the IEC 61850 protocol is GOOSE messaging, which enables ultra-fast, deterministic communication between IEDs. This feature is crucial for protective relaying and real-time system response.
GOOSE is used for event-driven messaging with millisecond latency.
IEDs can send and receive multicast messages, allowing instant coordination of devices during fault conditions.
GOOSE supports breaker interlocking, trip signals, and status broadcasts across the substation Ethernet network.
Process Bus vs. Station Bus: Streamlining Substation Design
Modern substation design increasingly depends on separating logical functions into dedicated communication layers. The IEC 61850 protocol facilitates this through its dual-bus architecture, improving flexibility and reducing costs.
The station bus handles monitoring, metering, and supervisory control via MMS messages.
The process bus connects high-voltage equipment to IEDs using digitized sampled values, eliminating the need for complex analog cabling.
This architecture reduces physical wiring, enhances signal accuracy, and supports remote diagnostics and maintenance.
Future-Proofing Substations with IEC 61850
As electric utilities face growing complexity from distributed energy resources, aging infrastructure, and cybersecurity threats, IEC 61850 provides a path forward. Its modular design and upgrade-friendly structure make it well-suited for evolving grid demands.
Easily supports DER integration, such as solar, wind, and battery systems
Enables wide-area monitoring systems (WAMS) and real-time situational awareness
Facilitates edge computing and virtualized protection systems
Compatible with ongoing enhancements in digital security and network segmentation
The IEC 61850 protocol is the cornerstone of modern substation automation, providing a robust, interoperable, and future-ready platform for intelligent grid operations. With features like GOOSE messaging, process bus architecture, and standardized data models, it enables faster fault response, reduced engineering effort, and seamless integration of diverse systems.
As the power grid evolves to accommodate renewable energy, electrification, and decentralization, IEC 61850 remains essential to building safe, smart, and scalable digital substations.