FERC Complaint Targets Duke, PJM Transmission Planning
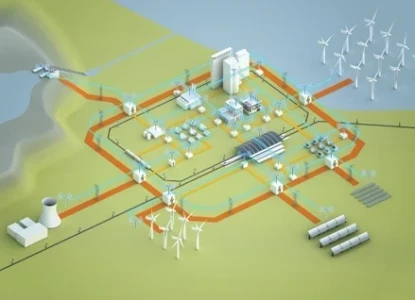
A coalition of large energy consumers and ratepayer advocates has filed a complaint with the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC), urging the agency to prohibit transmission owners from independently planning "local" transmission projects exceeding 100 kilovolts (kV). The coalition argues...